Bilayer Lead Aprons for Radiation Protection
11.21.23 | Tuesday | Jordan Houri, BSc, MSc
Bilayer lead – Transforming Lead Garments for Superior Radiation Protection
Traditional lead garments have been the standard in radiation protection for years, but their design has remained largely unchanged. Cumbersome and heavy, these standard aprons only protect the user’s front, leaving other critical areas exposed and vulnerable.
Explore the Future of Radiation Protection – Discover how StemRad redefines safety standards and what’s the minimum thickness of lead apron? Explore our innovative bilayer lead aprons and see the difference.
The Critical Need for Comprehensive Radiation Protection
Medical professionals routinely use X-rays for diagnostics and surgical procedures. While patient exposure is minimal, healthcare workers face a different challenge. Continuous exposure, even at low levels, can lead to cellular mutations and increase cancer risks. This reality highlights the need for effective and comprehensive protective measures. Enter bilayer lead technology – the new standard in full-body radiation shield.
Customize Your Safety
Ready for a radiation protection solution that fits your needs perfectly?
Contact us now to customize your bilayer lead gear.
Dual-Layer Defense: Understanding Bilayer Lead
Bilayer lead technology is a game-changer in radiation protection. As the name implies, it offers dual-layered shielding, ensuring front and back coverage. This innovative design employs two layers of radiation-attenuating materials, forming a protective cocoon that minimizes scatter and direct radiation exposure to as low as reasonably achievable levels.
Learn More with Our Experts
Have more questions? Our experts are here to help. Schedule a free consultation and learn more about the benefits of bilayer lead technology for your medical practice.
Efficient Protection with Bilayer Lead
Lead, known for its density and atomic number, has been the primary material for blocking gamma rays and X-rays.
Bilayer lead enhances this protection by doubling the layers. At StemRad, our MD garment sets a new benchmark with a 0.50 mm lead equivalent on the front and sides and an impressive 1.0 mm in the critical front overlap area.
Ergonomic and Effective: Rethinking the Weight of Lead Protection
The traditional approach to radiation safety has been to encase medical staff in heavy lead aprons, a necessary but not always practical solution.
Recognizing the ergonomic challenges, StemRad has reimagined lead aprons for radiation protection.
Our MD garment offers a strategic layering that ensures vital areas are shielded effectively without the added bulk. We’ve doubled the minimum protection standard to 0.50 mm on the front and sides and quadrupled it to 1.0 mm in the most critical areas.
This innovative design dramatically reduces the overall weight and distributes it more evenly, enhancing comfort without compromising on safety.
The Future of Radiation Safety: A Weightless Solution
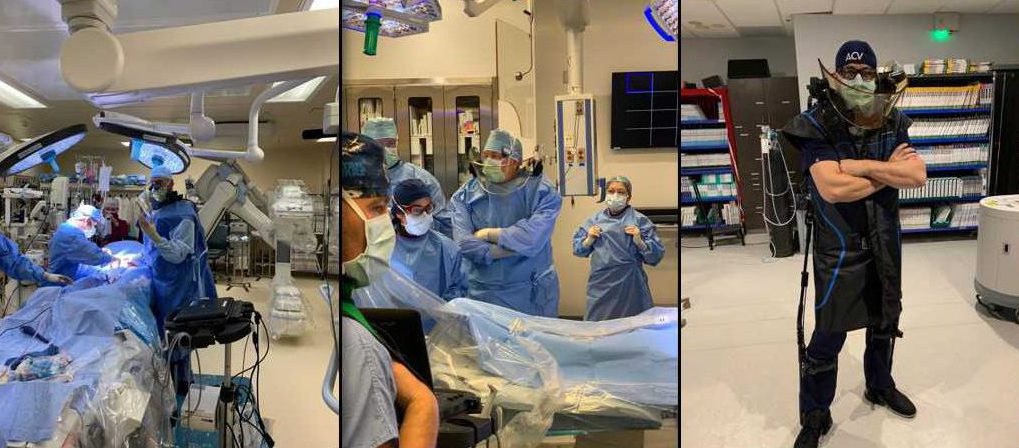
Physicians face the constant threat of X-ray radiation during medical procedures. Traditional lead aprons, used for shielding, are cumbersome and heavy, taking a toll on their health. Bilayer lead technology offers a revolutionary solution: lighter, more comfortable gear with enhanced X-ray protection. StemRad’s bilayer lead apparel is a prime example, prioritizing both safety and physician well-being.
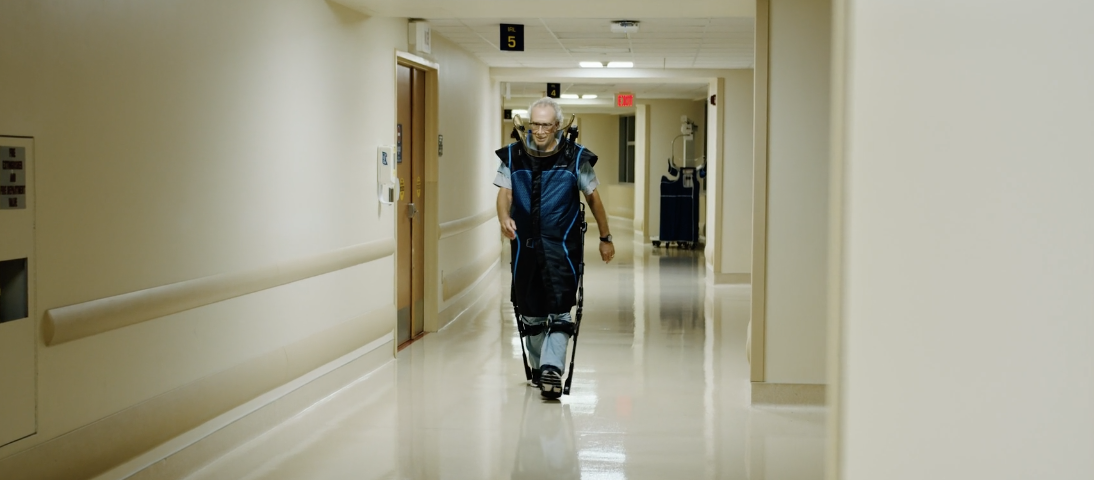
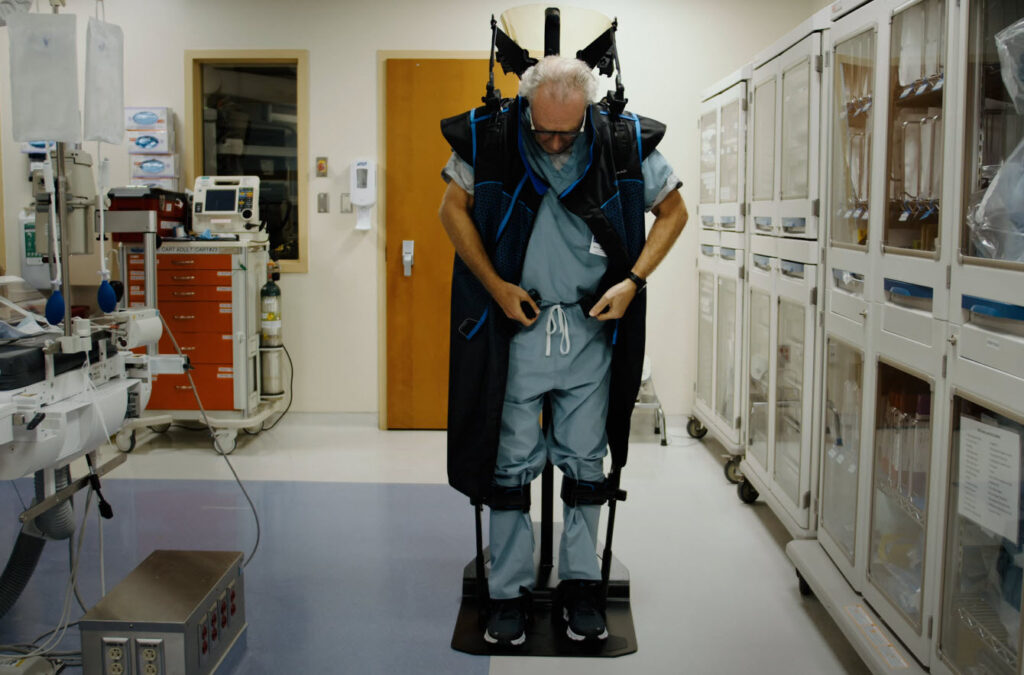
StemRad is pioneering a new era in radiation protection with our MD propriety exoskeleton technology. Traditional lead-lined gear, known for its heaviness, can be a burden over extended periods.
Our bilayer lead aprons for radiation protection, while lighter, still posed ergonomic challenges. Addressing this, the StemRad MD exoskeleton revolutionizes radiation protection by effectively removing the weight burden from the user, ensuring freedom of movement and superior protection.
Join the revolution in radiation protection.
Check out our press room to stay updated on the latest advancements in bilayer lead technology.
Elevating Comfort and Precision in Radiation Protection
At StemRad, we offer much more than radiation protection; we enhance the working experience for medical professionals. The MD exoskeleton is engineered for maximum comfort and precision. By eliminating up to 100% of the lead weight from the user’s body, we ensure that medical teams can easily and accurately focus on their critical tasks.
Discover the StemRad MD Exoskeletal System
Learn more about how the StemRad MD Exoskeletal System is setting new standards in radiation protection, blending cutting-edge technology with ergonomic design for the ultimate safety and comfort.
Frequently Asked Questions: Demystifying Lead Protection
Does wearing lead protect from radiation?
Absolutely. Lead is renowned for effectively blocking X-ray radiation, providing substantial protection in medical settings. This traditional shielding material remains a cornerstone in radiation safety practices.
How thick should lead be for effective radiation protection?
The efficacy of lead as a shield against X-rays increases with its thickness. In standard fluoroscopy procedures, a lead thickness of approximately 0.25 mm is generally sufficient to halve the radiation exposure. At StemRad, we go beyond the basics, offering enhanced protection with our bilayer technology.
Why is lead the preferred material for radiation shielding?
Lead’s exceptional X-ray attenuation coefficient makes it the ideal material for radiation protection. Its softness adds another advantage, allowing for more flexible and comfortable protective garments.
What makes bilayer lead more effective than traditional lead aprons?
The bilayer lead solution by StemRad incorporates an additional 0.50 mm of lead, effectively doubling the protection in crucial areas. This advanced approach ensures comprehensive coverage without compromising on comfort or mobility.
Can lead block other forms of radiation, like alpha particles?
While lead is effective against X-rays and gamma rays, it is not optimal for blocking charged particles like alpha radiation. Materials with a high hydrogen density, such as HDPE used in our AstroRad vest, are more suitable for these scenarios.
How does bilayer lead compare in protecting against solar radiation?
Lead offers some protection against solar-charged particle radiation, but for optimal shielding in these cases, materials like HDPE, with a high hydrogen density, are more effective. This principle is applied in our innovative AstroRad vest for space missions.
What sets StemRad’s bilayer lead technology apart in radiation protection?
StemRad’s bilayer lead technology represents a breakthrough in radiation safety. By providing dual-layer shielding, it offers comprehensive protection, covering both front and back, a significant advancement over traditional single-layer aprons. This innovative approach ensures maximum safety for medical professionals in X-ray environments.
How does the comfort of StemRad’s gear compare to traditional lead aprons?
Comfort and ergonomics are at the heart of StemRad’s design philosophy. Unlike traditional heavy lead aprons, our bilayer lead gear, supported by an exoskeletal structure, distributes weight evenly, reducing physical strain and pressure points. This means medical staff can wear our gear for longer without discomfort, ensuring consistent protection.
Can StemRad’s bilayer lead gear be tailored to individual needs?
We have created a versatile solution for medical professionals. StemRad offers effective radiation protection to medical personnel with our proprietary bilayer lead gear to fit individual requirements, enhancing comfort and protection. Since an exoskeleton bears the full weight of the radiation protection devices, the medical professional can function without impediment.

Lead Scientist, Space Exploration