The Importance of Lead Aprons in Radiology
11.01.23 | Wednesday | Jordan Houri, BSc, MSc
Welcome to the Frontier of Radiation Safety: StemRad’s Radiology Lead Aprons
At StemRad, we understand that in the world of interventional radiology, where C-arm fluoroscopy is a cornerstone, protection from ionizing radiation is paramount.
Close proximity to the X-ray source and the patient makes scatter radiation a real concern for healthcare professionals. That’s why we have designed our radiology lead aprons to be an essential part of your safety gear.
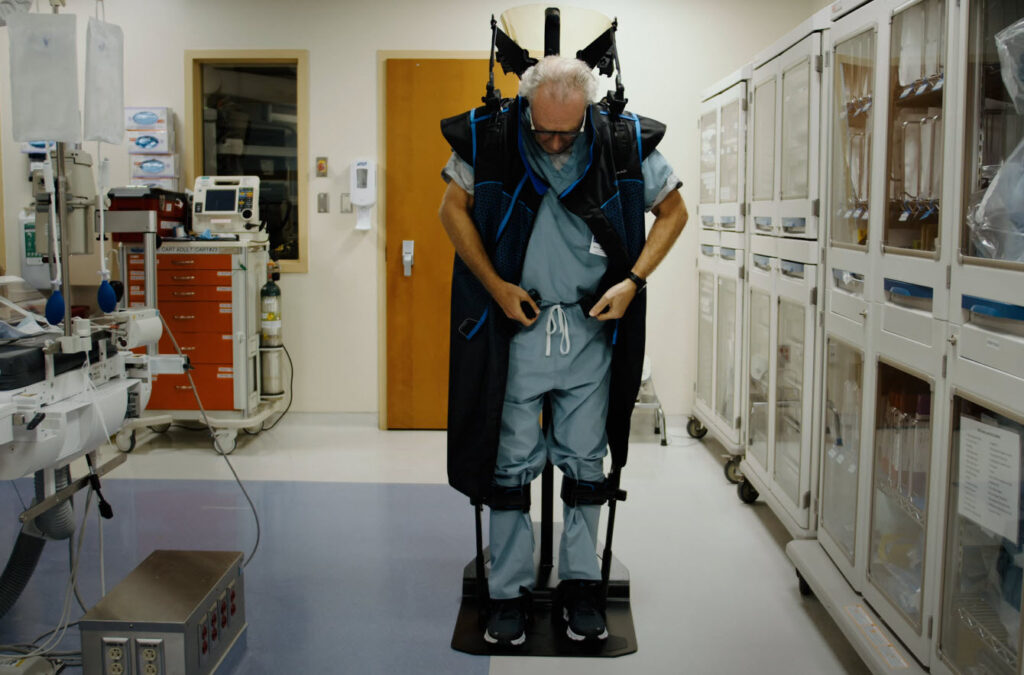
Advanced Lead Apron Used in the StemRad MD
Why Choose StemRad’s Radiology Lead Aprons?
We set the gold standard in radiological protection.
Our radiology lead aprons are meticulously engineered, offering superior shielding without sacrificing comfort.
They offer robust protection, with enhanced safety measures designed to give you peace of mind while you provide critical care.
Our comprehensive suite of protective gear doesn’t stop at aprons; we offer a variety of specialized gear designed to protect you from dangerous radiation.
Adapting to New Understandings in Radiation Safety
In a constantly evolving landscape, it’s important to stay updated on the latest in radiation safety. For example, UI Health Care recently adjusted its guidelines, moving away from lead shields for certain patient categories.
As Stephen Graves, PhD, from the University of Iowa, points out, technological advances have considerably reduced the radiation dose from imaging procedures. However, for medical professionals who are frequently in the radiation field, our radiology lead aprons remain non-negotiable.
In industries with ionizing radiation, like healthcare and research, professionals put themselves at risk daily. Traditional methods to shield from radiation were often bulky and cumbersome. That’s where StemRad steps in. We’ve innovated radiology lead aprons that make significant strides in safety and wearability.
Comprehensive Radiation Protection in Radiology
Let’s cut to the chase: radiology environments are a hotbed for ionizing radiation.
Not only do you need top-notch radiology lead aprons, but you also require additional gear to guarantee total safety.
StemRad offers a complete portfolio of high-end products for your protection. There’s no room for compromise in personal radiation safety.
What Exactly is a Radiology Lead Apron?
Radiology lead aprons are categorized as specialized Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) crafted to block radiation exposure.
These are no ordinary garments.
In our lead gowns we use a lead-free bismuth-antimony bilayer.
This is the most effective lightweight material for x-ray protection. designed to be flexible yet robust, effectively shielding the vital organs.
The designs are so varied they cater to a broad spectrum of needs without compromising mobility.
Also being lead-free really helps with disposal of old product.
Components That Make Up Our Lead Aprons
StemRad’s lead aprons set a new benchmark in radiation protection. Expertly crafted, these lead aprons represent a fusion of safety, utility, and mobility. They offer an unparalleled all-in-one solution. The innovative exoskeleton ensures the weight is evenly distributed, negating the need for multiple segmented units.
A significant distinction lies in our integrated thyroid collar, seamlessly incorporated into our lead aprons, eliminating the reliance on separate accessories. Moreover, our visor enhances radiation protection, providing superior shielding and unparalleled visibility — a marked advancement from conventional lead goggles.
At the core of our commitment is excellence. Each of StemRad’s lead aprons and radiation protection solutions stems from rigorous research, thorough testing, and detailed analysis. We stand tall and proud to offer among the world’s most effective and reliable radiation protection solutions.
Why Choose a StemRad Lead Apron?
Unmatched Safety: Our radiology lead aprons are light, well designed and can attenuate over 90% of radiation at 80 kVp levels.
Long-term radiation exposure has serious consequences. Using our gowns reduces your risk substantially.
All About Comfort: Say goodbye to the bulky, inhibiting lead aprons of old. Our modern designs are light, facilitating ease of movement while you focus on your tasks.
Cutting-Edge Lead Apron Innovations
StemRad MD – An exoskeleton-based masterpiece freeing you from weight constraints while allowing unparalleled movement in the Operating Room (OR).
Exoskeleton Support: This is a proprietary exoskeleton that cuts down the weight burden and offers full head protection, with an integrated thyroid collar.
Innovative Gear, Tailored Solutions
We know that one size doesn’t fit all.
That’s why StemRad offers bespoke solutions that adapt to your needs. From pediatric care to complex surgical procedures, we’ve got you covered, literally.
User Experience & Training
Getting the best gear is half the battle. Knowing how to use it effectively is equally important. That’s where our training modules come in, turning your team into knowledgeable users of radiation protection gear.
Future-Proofing Radiation Safety
As technologies advance, StemRad is at the forefront, researching and developing next-gen products. We’re committed to evolving with the needs of the healthcare industry. Our aim is to one day make radiation exposure a thing of the past.
StemRad’s comprehensive approach to radiation safety is changing the game. From advanced lead aprons to a full suite of supporting gear, we’ve set a new standard in radiological protection.
FAQs About Radiology Lead Aprons
- What’s a Typical Apron Weight?
Weight ranges from 5 to 25 pounds. The StemRad MD uses an exoskeleton to offset this.
- Why use Lead Aprons?
Lead (Pb) excels in high atomic number (82) and density, making it a prime material for blocking X-rays and gamma rays.
- Who Should Wear a Radiology Lead Apron?
If you’re not a patient and you’re in a room where radiation is present, you need to be wearing one.
- What’s the Ideal Dental Apron Thickness
For dental settings, the apron should offer protection equivalent to 0.3 mm of lead.
- Are There Lead-Free Options Available?
These are thicker alternatives comprised of different heavy metals but without toxic lead.
Our radiation protection gear is your best choice for unparalleled safety and comfort. Stay safe with StemRad radiology lead aprons.

Lead Scientist, Space Exploration